horses pelvis info...
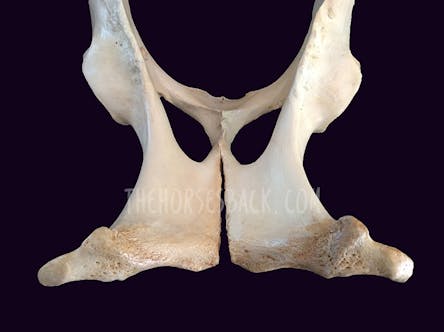
The pelvis in a horse, as in many mammals, is a bony structure that forms the hind end of the vertebral column and is essential for supporting the weight of the horse's body and facilitating movement. Here's some information about a horse's pelvis:
- Anatomy:
The equine pelvis is composed of several bones that are fused together to create a strong and sturdy structure. The main bones of the horse's pelvis include the ilium, ischium, and pubis. These bones form a bony ring that encircles the pelvic cavity.
- Function:
The horse's pelvis serves several important functions:
- Weight Bearing:
The pelvis supports the weight of the horse's body and helps distribute it evenly across the hind limbs.
- Attachment Point for Hind Limb Muscles:
The pelvic bones provide attachment points for the powerful muscles of the hindquarters, which are crucial for movement and propulsion.
- Protection of Internal Organs:
The pelvic cavity protects internal organs, including the bladder and reproductive organs, from external injury.
- Structure:
The pelvis is a complex structure with distinct regions, including the ilium, ischium, and pubis. The sacroiliac joint connects the pelvis to the lumbar spine, forming the sacrum. The sacroiliac joint is important for stability and movement of the hind end
- Reproduction:
In mares, the pelvis plays a critical role in the birthing process. The size and shape of the pelvic canal can affect a mare's ability to foal naturally, and veterinarians often assess this when assisting with breeding and foaling.
- Injuries and Issues:
Horses can experience injuries or issues related to the pelvis, such as fractures, arthritis in the sacroiliac joint, or pelvic misalignments. These issues can cause lameness and discomfort and may require veterinary evaluation and treatment.
- Lameness:
Pelvic issues can contribute to hind end lameness in horses, affecting their performance and overall well-being. Diagnosing the source of the lameness is essential for appropriate treatment.
- Veterinary Care:
Veterinarians use various diagnostic tools, such as X-rays and ultrasound, to evaluate the horse's pelvis if there are concerns or issues. Treatment options may include rest, physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, or, in some cases, surgical intervention.



