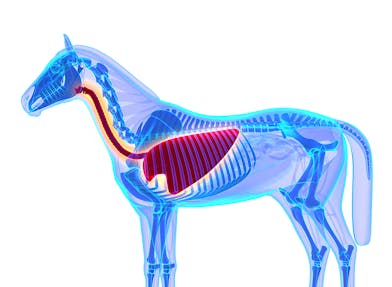
rib cage info...
The rib cage of a horse is a vital component of its skeletal system, serving several important functions in support, protection, and respiration. Here is some information about a horse's rib cage:
- Structure and Composition: A horse's rib cage consists of a series of ribs, which are long, curved bones that form a protective cage around the vital organs in the horse's chest, including the heart and lungs. Horses typically have 18 pairs of ribs, although the number can vary slightly among individuals.
- Attachment to the Spine: The ribs are attached to the horse's thoracic (chest) vertebrae along the dorsal (back) part of the vertebral column. Each rib is connected to a specific thoracic vertebra through joints called costovertebral joints.
- Sternum (Breastbone): The ribs of a horse are connected at the front of the body to the sternum or breastbone. The sternum forms the ventral (front) part of the rib cage and provides additional structural support.
- Function: The primary function of the rib cage is to protect the vital organs in the thoracic cavity, particularly the heart and lungs. It acts as a bony shield, helping to safeguard these organs from external trauma.
- Breathing: The rib cage plays a crucial role in the horse's respiratory system. As horses breathe, the contraction and expansion of the rib cage, along with the diaphragm, create changes in thoracic pressure, allowing air to be drawn into and expelled from the lungs.
- Costal Cartilages: The ribs are connected to the sternum through cartilaginous extensions known as costal cartilages. These cartilages provide flexibility to the rib cage, allowing it to expand and contract during breathing.
- Ribs and Movement: Horses have a rigid rib cage compared to some other animals. While they have some degree of rib mobility during respiration, their primary mode of breathing relies more on the diaphragm's movement than on the expansion and contraction of the rib cage.
- Muscles: The muscles between the ribs (intercostal muscles) aid in rib movement during breathing. Muscles such as the diaphragm, abdominal muscles, and various accessory respiratory muscles also contribute to breathing efficiency.
- Horse Health: The condition of a horse's rib cage can impact its overall health. Injuries to the ribs or sternum can be painful and affect a horse's performance. Additionally, certain diseases and conditions, such as pleuritis (inflammation of the pleura, the membrane around the lungs), can affect the functioning of the rib cage and the horse's ability to breathe comfortably.
- Radiographic Examination: Veterinarians may use radiography (X-rays) to assess the condition of a horse's rib cage, particularly if there are concerns about fractures, injuries, or respiratory issues